
This website uses cookies to obtain information about your general internet usage. App Store is a service mark of Apple Inc. Apple, iPad, and iPhone are trademarks of Apple Inc., registered in the U.S. Telephone calls and online chat conversations may be recorded and monitored.
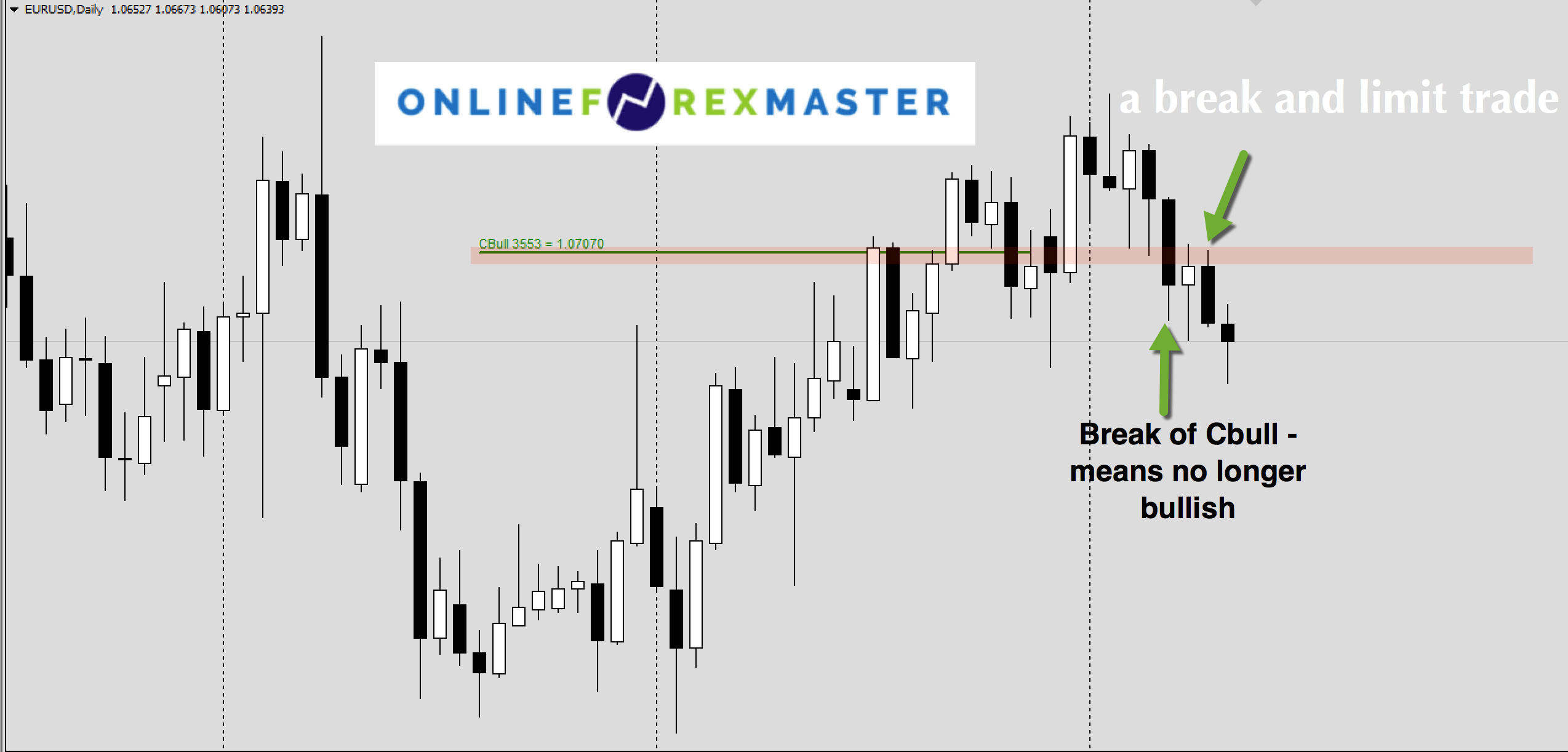
#LIMIT TRADING REGISTRATION#
CMC Markets UK Plc and CMC Spreadbet plc are registered in the Register of Companies of the Financial Conduct Authority under registration numbers 173727. CMC Markets Germany GmbH is a company licensed and regulated by the Bundesanstalt für Finanzdienstleistungsaufsicht (BaFin) under registration number 154814. You should consider whether you understand how spread bets and CFDs work and whether you can afford to take the high risk of losing your money.ĬMC Markets is, depending on the context, a reference to CMC Markets Germany GmbH, CMC Markets UK plc or CMC Spreadbet plc. 71% of retail investor accounts lose money when spread betting and/or trading CFDs with this provider. Spread bets and CFDs are complex instruments and come with a high risk of losing money rapidly due to leverage. Then, exposure to each asset class would be 33.3%. An alternative would be to divide the portfolio across stocks, bonds and property, with an equal weighting to each. If an investor only owned stocks, the exposure to stocks is 100%. An investor could also diversify by asset class to reduce exposure.

That would result in 25% exposure to each ETF trade and would reduce the risk of the portfolio. Similarly, instead of just owning one exchange-traded fund (ETF) and having a 100% exposure to that ETF, an investor could buy four different ETFs. This would significantly reduce the stock-specific risk within the portfolio. This would result in a stock exposure of just 5% per stock. For example, instead of just owning one stock and having a 100% exposure to that stock, an investor could buy 20 different stocks. This involves having a variety of different investments in one portfolio. Exposure can be reduced by selling an asset, by diversification or through hedging.Īnother way to reduce financial exposure is through diversification. To lower risk, investors need to ensure that they are not overexposed to any particular investment type. A risk averse investor may have 80% of his portfolio in bonds and only 20% in equities. In contrast, risk-averse investors often have less exposure to equities and more exposure to bonds. Because equities are more risky than bonds, these investors face higher total portfolio risks. Investors that are comfortable with risk often allocate a higher proportion of their portfolio to equities, and a smaller proportion to bonds. If equities perform poorly, the portfolio with the 100% weighting to equities is likely to perform worse than the portfolio with 60% exposure to equities. For instance, a portfolio with 100% exposure to equities has a higher risk from equities than a portfolio with 60% exposure to equities and 40% exposure to bonds. The higher the exposure to a particular investment in percentage terms, the higher the risk associated with that investment. This investor might allocate 15% of their portfolio to technology stocks and 0% to utility stocks.

Similarly, consider an investor who is bullish on technology stocks, but bearish on utility stocks. The exposure to US stocks is higher because the investor expects this region to do well. This investor might allocate 30% of their portfolio to US stocks and 10% to European stocks. Here’s an example of breaking down market exposure: consider a UK investor who is bullish on US stocks and neutral on European stocks. In other words, if someone expects a particular investment to perform well, they will have a higher exposure to the investment, relative to other investments. In general, if a trader is bullish on a particular asset, he will have a larger exposure to the asset than he would if he was neutral or bearish towards the asset. Exposure depends on an individual’s goals and risk tolerance.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
